


 |
 |
 |
|
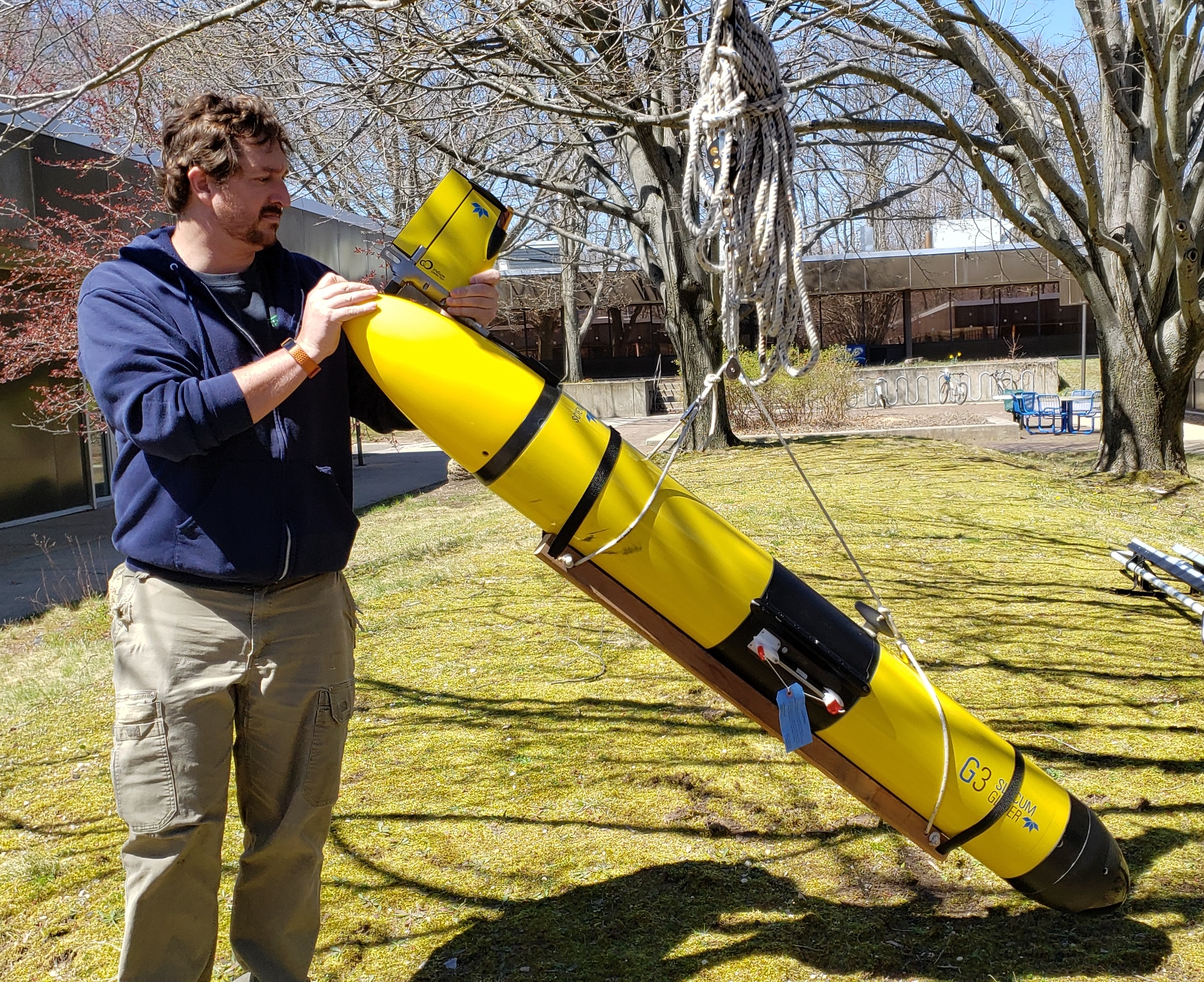
SoMAS Ocean Glider Project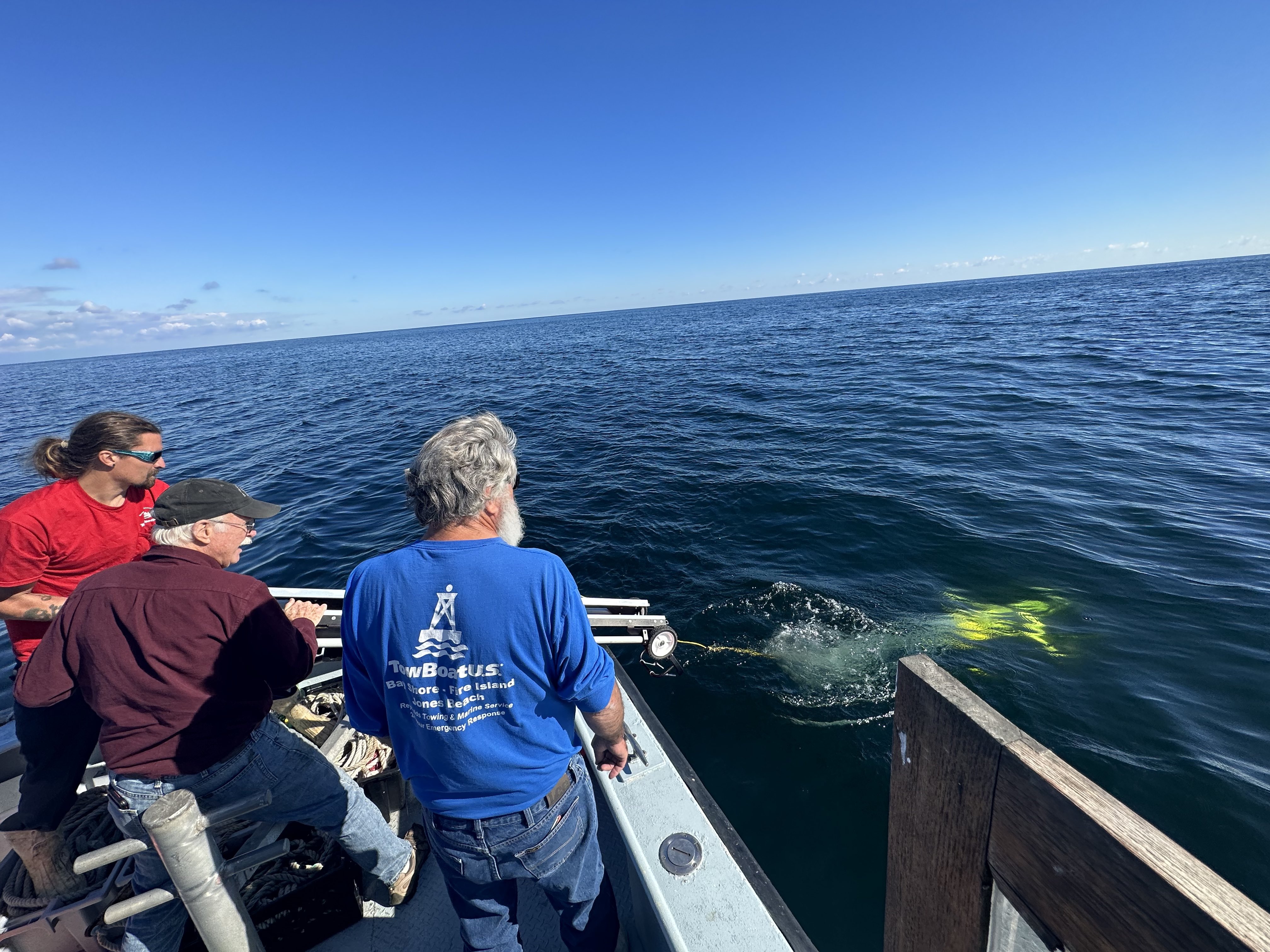 
 ** Picture by Charlie Flagg Charles
N. Flagg
Charles.Flagg@stonybrook.edu Jack McSweeney Jack.Mcsweeney@stonybrook.edu Lucas Merlo Lucas.Merlo@stonybrook.edu Matt Learn Mathew.Learn@stonybrook.edu |
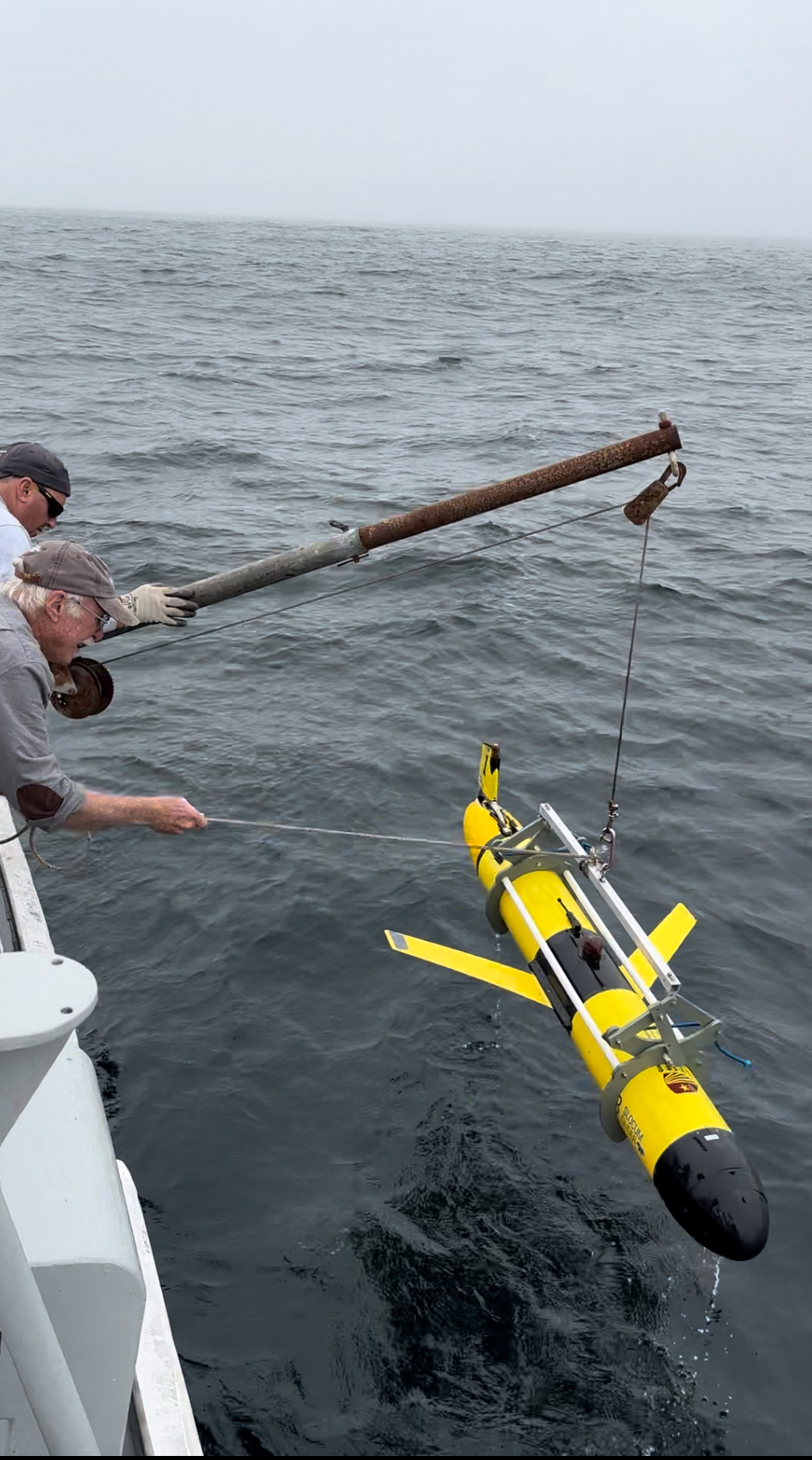 Glider Recovery using grabber 
Compass
calibration
|
Overview
The glider project at Stony Brook University grew out
of the New York Department of Conservation's need to
understand and monitor the New York Bight and its long-term
health and productivity. As a result, the School of
Marine and Atmospheric Sciences at Stony Brook University
developed a ten year program to measure the hydrography,
chemistry and fishery biomass from seasonal cruises on the
RV Seawolf and ~30 day ocean glider cruises covering the New
York Bight area. Subsequently, a collaborative program
between Rutgers, Stony Brook and the University of Maine was
proposed to NOAA to use the gliders that were being deployed
in the Middle Atlantic Shelf and the Gulf of Maine to
monitor ocean acidification in the area. The ocean
acidification monitoring makes use of a new pH sensor
developed by Sea Bird Electronics, in collaboration with
Grace Saba's group at Rutgers, that can be mounted on the
gliders. This new sensor has been added to the Stony
Brook glider with its first cruise starting February, 2021.
The
SoMAS ocean glider operation is intended to provide long
term and seasonal data of the basic physical conditions in
the New York Bight as part of the New York DEC's ocean
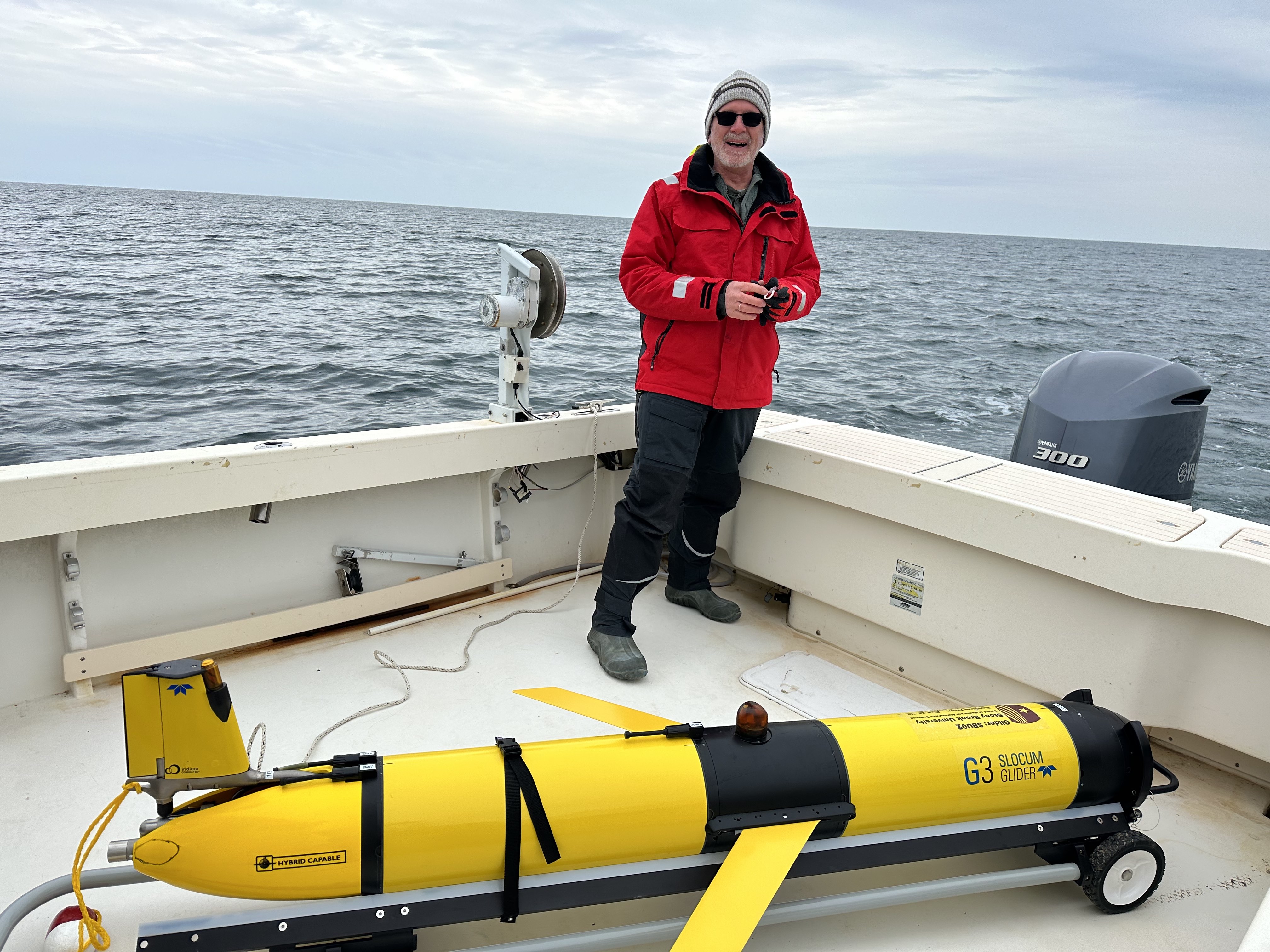
monitoring effort. The glider, SBU01, is a Webb
Research Slocum G3 shallow water unit, maximum depth is
350m, equipped with the standard suite of sensors measuring
temperature, conductivity, pressure, dissolved oxygen,
chlorophyll fluorescence and turbidity. The intent is
to deploy the glider seasonally from south of Long Island on
a cruise that includes a series of transects out to the edge
of the continental shelf ending up off Sandy Hook or Little
Egg Inlet, New Jersey for retrieval. The glider
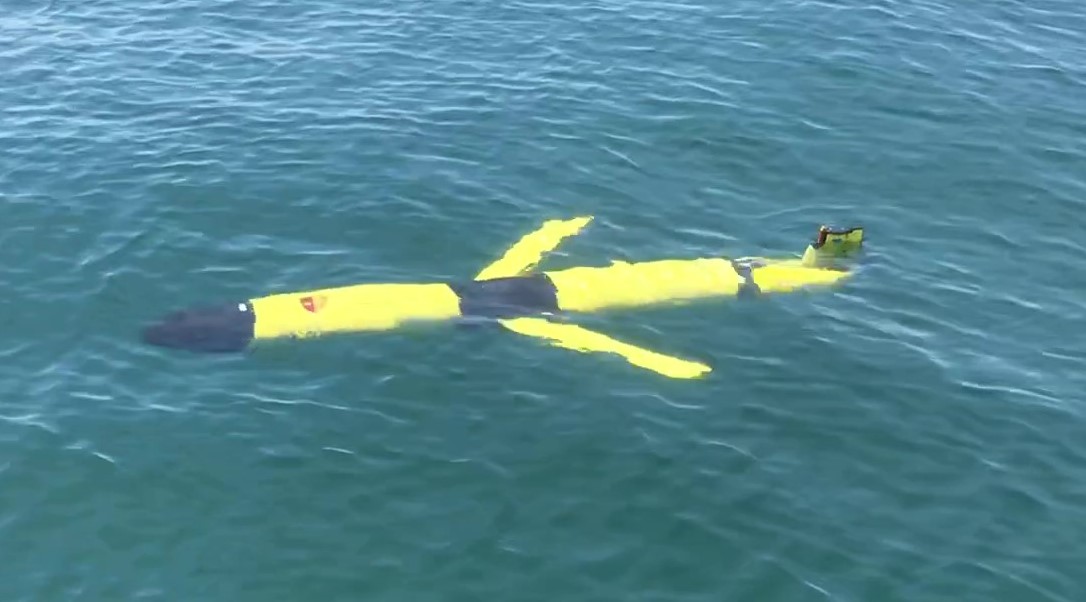
propels itself through a series of dives and climbs making
about 20 km per day, slower in shallow water, faster in deep
water with fewer dive/climb iterations. With the
rechargeable batteries in the glider, cruise duration in MAB
waters is about 32 days and ~600 km. So far, there
have been six cruises in the MAB, shown below, adding more
than 13,000 vertical profiles of T, S, O2, Fl and Turbidity
to the database. In January the SeaBird CTD/pH sensor
was added to the glider to provide seasonal and spatial
distributions of pH to assist in monitoring the impact of
CO2 absorption in the ocean.
Piloting
of the glider is accomplished through a two-way Iridium
satellite connection initiated by the glider when it
surfaces at approximately three hour intervals. Using
Webb Research supplied software, the Slocum Fleet Mission
Control or SFMC, heavily decimated realtime data are sent
ashore and mission modifications can be sent to the
glider. The near realtime data that have been uploaded
from the glider are currently being minimally processed by
Rutgers' glider group into netcdf files for each surfacing
and uploaded onto NOAA's ERDDAP server accessible via
https://marine.rutgers.edu/cool/data/gliders/deployments.
Post
cruise, the complete set of glider data are offloaded from
the glider's memory cards and processed using a set of
routines based upon those developed by John Kerfoot
(Rutgers), Robert Todd (WHOI) and Ruth Curry (BIOS).
That processing system calibrates the data, does a QA/QC
check on the validity of the results and stores the data in
a large Matlab file. The Matlab files are accessible
through the project server. Matlab files are also
converted to the a netcdf file format and uploaded onto
NOAA's ERDDAP server (link below). The glider data is
so voluminous that using the ERDDAP server is the only
practical way of making the data available to potential
users.
June,
2022, Glad to report that SBU01 has finally returned from a
long sojourn at Webb for calibration and checkup. Next
deployment is scheduled for mid_July.
A
new G3s Slocum glider,designated SBU02, arrived in January
2023 to back-up and compliment SBU01. This glider has
an updated computer as the older computer in SBU01 is no
longer available. Virtually all the commands used in
the older version work with the new computer with some
additional capabilities, in particular the ability to
compress files sent over the satellite link. The
new G3s glider arrived in late January equipped with a
CTD/pH unit, a chlorophyll/turbidity sensor, a dissolved
sensor and the DMON2 passive acoustic sensor to listen
for whales of various kinds. A portion of output
from the DMON2 is telemetered ashore along with the
other decimated sensor data. The DMON2's internal
computer makes preliminary identifications of whale
calls which are then sent ashore to be assessed by Mark
Baumgartner's group at WHOI. Positive ID's of
whales then are broadcast to a user group that includes
the shipping industry in an effort to minimize ship
strikes.
As of March 2023, SBU01 has also been fitted
with a DMON2 and has been activated on subsequent
deployments, except for October 2023 deployment.
There are two main deployment paths for the
SBU gliders. For the NYDEC surveys, the main parameters
include deployment out of east Long Island, NY
(Shinnecock Inlet), traveling to the edge of the
continental shelf, crossing the Hudson Canyon, and being
recovered off the the coast of New Jersey to cover as
much of the NY bight as possible. For the NYSERDA
surveys, deployment is generally out of Fire Island
Inlet with the focus on covering as many tracks within
the offshore wind farm lease areas before being
recovered off of the coast of New Jersey. For all glider
deployments, the glider is generally released at a depth
of ~100 ft to enable sufficient testing before starting
the mission, as such the distance from shore varies
accordingly.
Deployments
Useful Websites:
ERDDAP Glider Data Portal Netcdf glider data visualization and download
Robots for Whales Real-time detected whale location, type, and signal origin
- NDBO Buoy 44025 Data from a 3-meter discus buoy South of Long Island.
- NDBO Buoy 44066 Data from a 3-meter discus by Hudson Canyon
- OceanWeather.com Click on the Current Marine Data and the corresponding area to see wave height and wind data over the oceans.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Remodeling Glider
Lab setup during Summer 2023
Updated lab setup
Glider ballasting
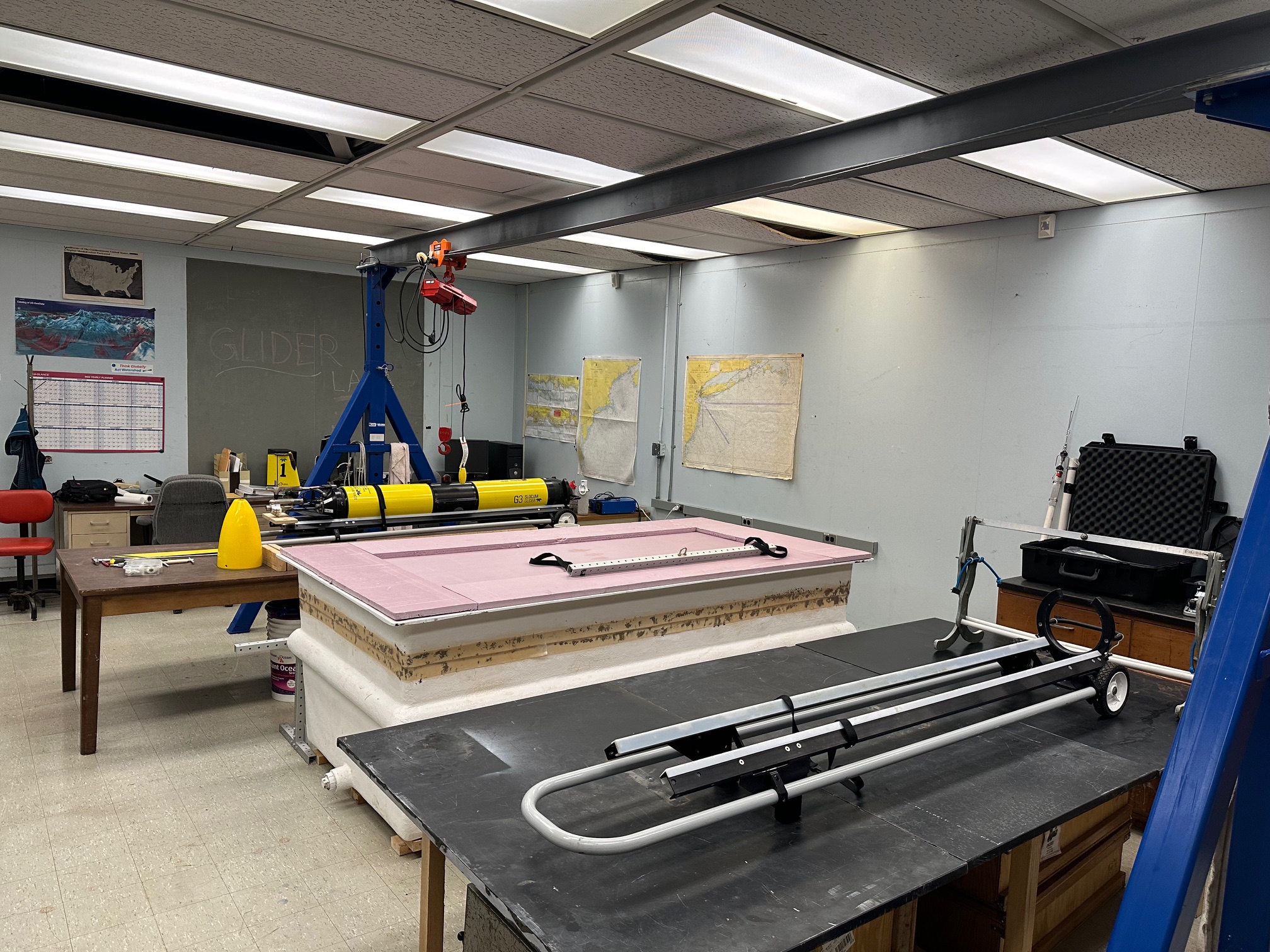



*All pictures taken by Maha Alnajjar except for
those marked with a double asterisk.